This is an old revision of the document!
Integration: Relational Databases
Overview | Servers | Environments | Queries | Updates | Generating Data Files | Implementation Guides
Environments and Relational Databases
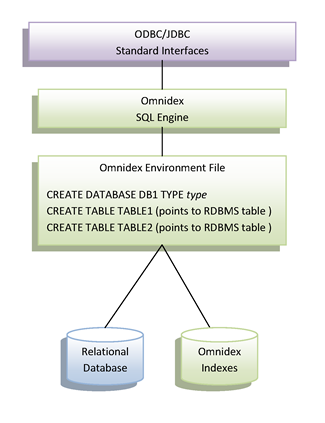
Omnidex provides access to relational database by creating an Omnidex Environment File that points to the database and the tables. Within the Omnidex Environment File, the administrator declares a database with connection information for the underlying relational database, and then declares tables that point to the underlying relational tables or views. Note that the Omnidex Environment File contains only metadata, and does not make a copy of the data in the relational database.
Omnidex only has access to the tables and columns that were declared Omnidex Environment File. Any database objects that exist in the underlying relational database do not become accessible to Omnidex until they are added to the Omnidex Environment File. The Omnidex Environment File can also be use to alter the metadata. Objects can have different names within Omnidex, and some datatypes can be changed as needed.
The indexes that are declared in the relational database should also be declared as NATIVE indexes in the Omnidex Environment File. Omnidex uses this information to determine the best optimization for a query and will relay queries directly to the relational database if this will improve performance. Omnidex also frequently retrieves primary keys from its own indexes and submits them to the relational database, requiring that the primary key be natively indexed to insure performance.
Combining Raw Data Files and Relational Databases
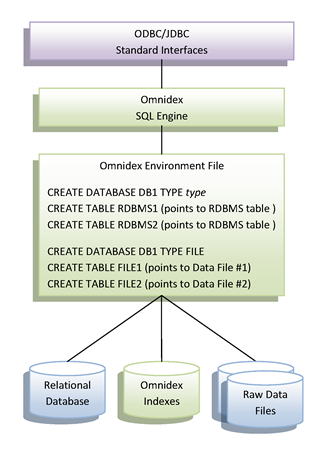
Raw data files often supplement a relational database. For example, a transaction log or a supplemental data file may contain information that is ideal to correlate with a relational database. Companies that have been importing that data into the relational database can avoid that extra work, and use Omnidex to join those two data sources together instead.
An Omnidex Environment File can include more than one database, and each database can be of a different type. An Omnidex Environment File can have one database that points to the underlying relational database, and a second database that points to a series of raw data files. When connected to this Omnidex Environment File, applications can issue SQL statements that join tables from both databases.
Once connected to this Omnidex Environment File, statements can be issued that reference all of the tables in the environment, including referencing tables from both databases.
Additional Resources
See also: