Integration: Relational Databases
MySQL
Overview | Environments | Databases | Tables | Constraints | Datatypes | Queries | Updates | Example
Overview
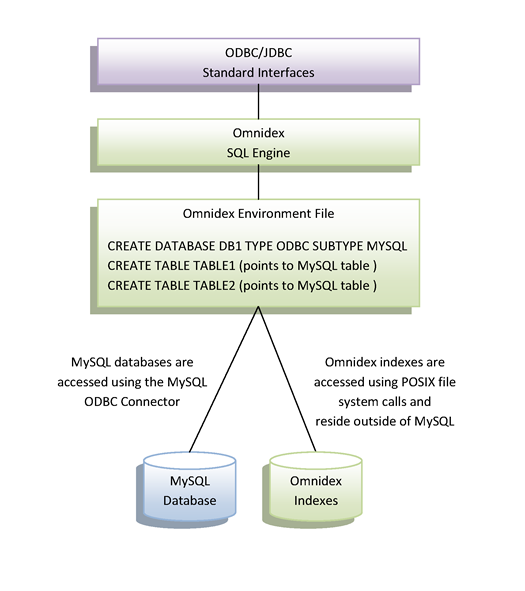
Omnidex can be deployed directly against a MySQL database. Omnidex retrieves and indexes the MySQL data, and queries read directly from the MySQL database as needed. This approach allows Omnidex to work alongside MySQL, providing a high-performance query environment for applications.
An Omnidex Environment File controls how Omnidex connects to the MySQL database and identifies the tables and columns that Omnidex will have access to. Omnidex accesses the MySQL data directly using standard SQL statements issued through the MySQL ODBC Connector. During indexing and query processing, Omnidex maintains a connection to the MySQL database and accesses the data as needed. Typically, queries are first routed to the Omnidex indexes where specific rowids or primary keys are identified that meet the criteria. Omnidex then fetches the appropriate rows using these values with standard SQL statements.
Omnidex does not migrate the data out of MySQL, but instead directly references the data in the MySQL database. This is not a requirement, though. Migration of the data into raw data files is an option if that is preferable. In fact, many companies use Omnidex Snapshots for this very purpose. Omnidex Snapshots are high-performing, highly-portable, heavily-indexed copies of data that can be easily accessed using standard ODBC and JDBC interfaces.
Omnidex is usually deployed on read-only tables. Most applications require tens to hundreds of Omnidex indexes on a table, making real-time updates impractical. Applications usually set aside certain MySQL tables that are refreshed on a regular basis and Omnidex indexes are completely refreshed. Omnidex does support real-time updates for those situations where there are fewer indexes and lower volume.
Additional Resources
See also: