This is an old revision of the document!
Integration: Relational Databases
Overview | Servers | Environments | Queries | Updates | Generating Data Files | Implementation Guides
Servers
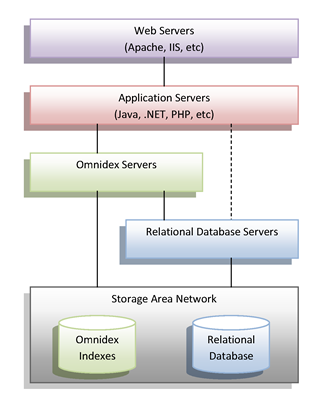
Omnidex benefits from being on a separate server from the relational database whenever possible. Relational databases usually adopt a strategy that consumes most of the resources on a server. It is not uncommon for a relational database to consume nearly all of the memory and CPU while processing large quantities of data using multiple threads. While this maximizes the performance of the relational database, it does not preserve many resources for other processes such as Omnidex.
Typically, Omnidex is placed on an Omnidex Server and the relational database is placed on a Relational Database Server. This each to utilize the system resources as they need without interference from the other. If all queries are to be satisfied by Omnidex, then the application simply switches the connections from the relational database to either Omnidex's ODBC or JDBC driver. Alternatively, the application can concurrently maintain connections directly to the relational database server.
Most companies rely on a Storage Area Network (SAN) for accessing their data. Omnidex indexes will usually reside on the SAN as well, though this is not a requirement. High-quality SAN's provide great flexibility and excellent performance, though it is important to insure sufficient cache in the SAN as well as sufficient number of paths to the servers.
Additional Resources
See also: